Nepal's economy is classified as lower-middle-income by the World Bank, with a GDP of approximately $40.61 billion (nominal) in 2022 [1] . Despite its developing status, Nepal is a frontrunner in adopting renewable energy sources.
Nepal's abundant rivers, thanks to its mountainous landscape, offer significant potential for hydropower generation [2] . Nepal is also exploring geothermal and wind energy resources to diversify its renewable energy mix. The government has set an ambitious target of achieving 100% renewable electricity by 20451.
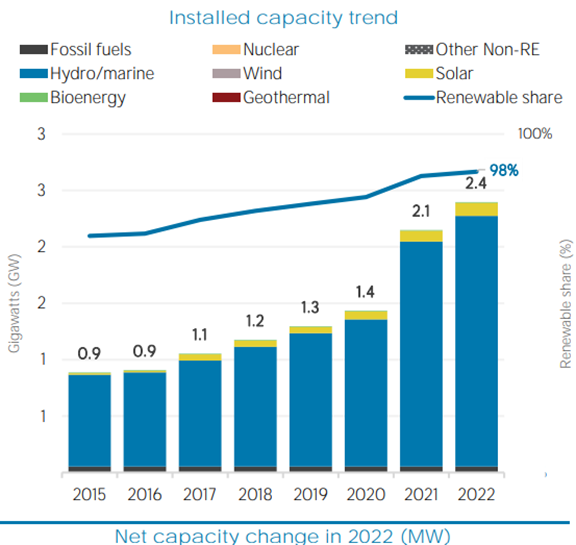
Several initiatives are underway to encourage renewable energy use. These include:
Nepal has set ambitious goals for decarbonisation and is a leader in promoting renewable energy within its power mix. Here's a breakdown:
Decarbonisation Goals:
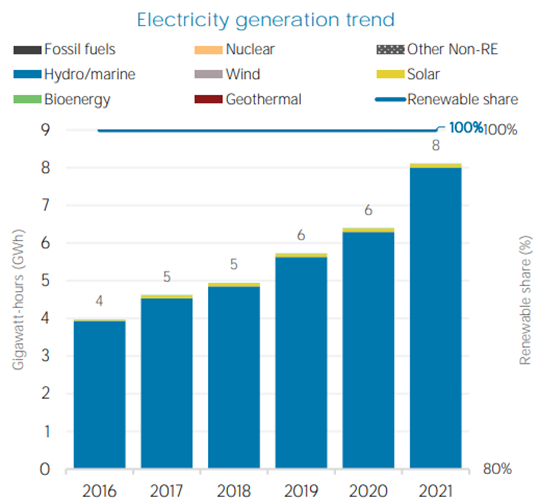
Fig 2: Electricity Generation trend in Nepal( IRENA 2022 )
To read a deep dive report of Nepal, click here
[2] International Renewable Energy Agency
[4] Clean Energy Transition Plan and Pathway
[5] Multi Actor Partnership for clean 100% renewable energy
In 2022, Nepal exported $4.62k in Hydrogen, making it the 144th largest exporter of Hydrogen in the world. At the same year, Hydrogen was the 511th most exported product in Nepal. The main destination of Hydrogen exports from Nepal are: Pakistan ($2.98k) and Canada ($1.64k).
The fastest growing export markets for Hydrogen of Nepal between 2021 and 2022 were Pakistan ($2.98k) and Canada ($1.64k).
In 2022, Nepal imported $1.48M in Hydrogen, becoming the 106th largest importer of Hydrogen in the world. At the same year, Hydrogen was the 535th most imported product in Nepal. Nepal imports Hydrogen primarily from: India ($1.24M), China ($149k), United Arab Emirates ($61.5k), Qatar ($12.5k), and France ($9.4k).
The fastest growing import markets in Hydrogen for Nepal between 2021 and 2022 were India ($185k), China ($88.1k), and United Arab Emirates ($61.5k).
Nepal's Green Hydrogen Policy (GHP) [1] , introduced in 2024, is a forward-thinking initiative aiming to leverage the country's abundant hydropower resources for clean energy production. Overall, Nepal's Green Hydrogen Policy represents a bold step towards a cleaner and more secure energy future. By addressing the challenges and ensuring effective implementation, Nepal can become a frontrunner in the green hydrogen revolution.
Policy Objectives [1] :
Potential Benefits:
While Nepal's Green Hydrogen Policy (GHP) was introduced in 2024, the specific details regarding the regulatory framework are likely still under development. The policy itself outlines the intention to establish a framework, but specifics might not be entirely finalized yet.
Possible Focus Areas of the Regulatory Framework:

Nepal is a country brimming with potential for renewable energy. Its unique geography and forward-thinking government policies position it to become a leader in clean energy production. However, limitations in infrastructure pose a challenge to fully unlocking this potential
Renewable Energy Potential:
Infrastructure Challenges:
N/A
Overall, Nepal's future in renewable energy is bright. By addressing infrastructure limitations and implementing effective policies, Nepal can become a leader in clean energy production.
There have been a couple of significant announcements regarding green hydrogen projects in Nepal: