New Zealand is an island located in the Southwest region of the Pacific Ocean. With a GDP of 247 billion [1] , New Zealand has the 52nd largest economy globally. New Zealand has a market economy, and the service sector makes up a large portion of the GDP. [2] The biggest industries in the country include the agricultural and horticulture sector, mining, and fishing industries. The country has one of the most globalised economies and depends greatly on international trade. [3]
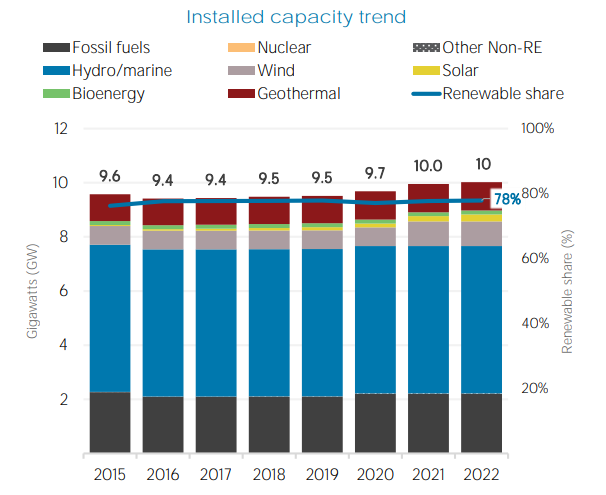
Fig 1: Installed capacity trend of New Zealand ( IRENA 2022 )
Renewable energy sources account for 40 percent of the total primary energy sources of New Zealand. This includes geothermal, hydro and wind. The other 60 percent of energy comes from oil (32 percent), natural gas (21 percent) and a small amount of coal. [4]
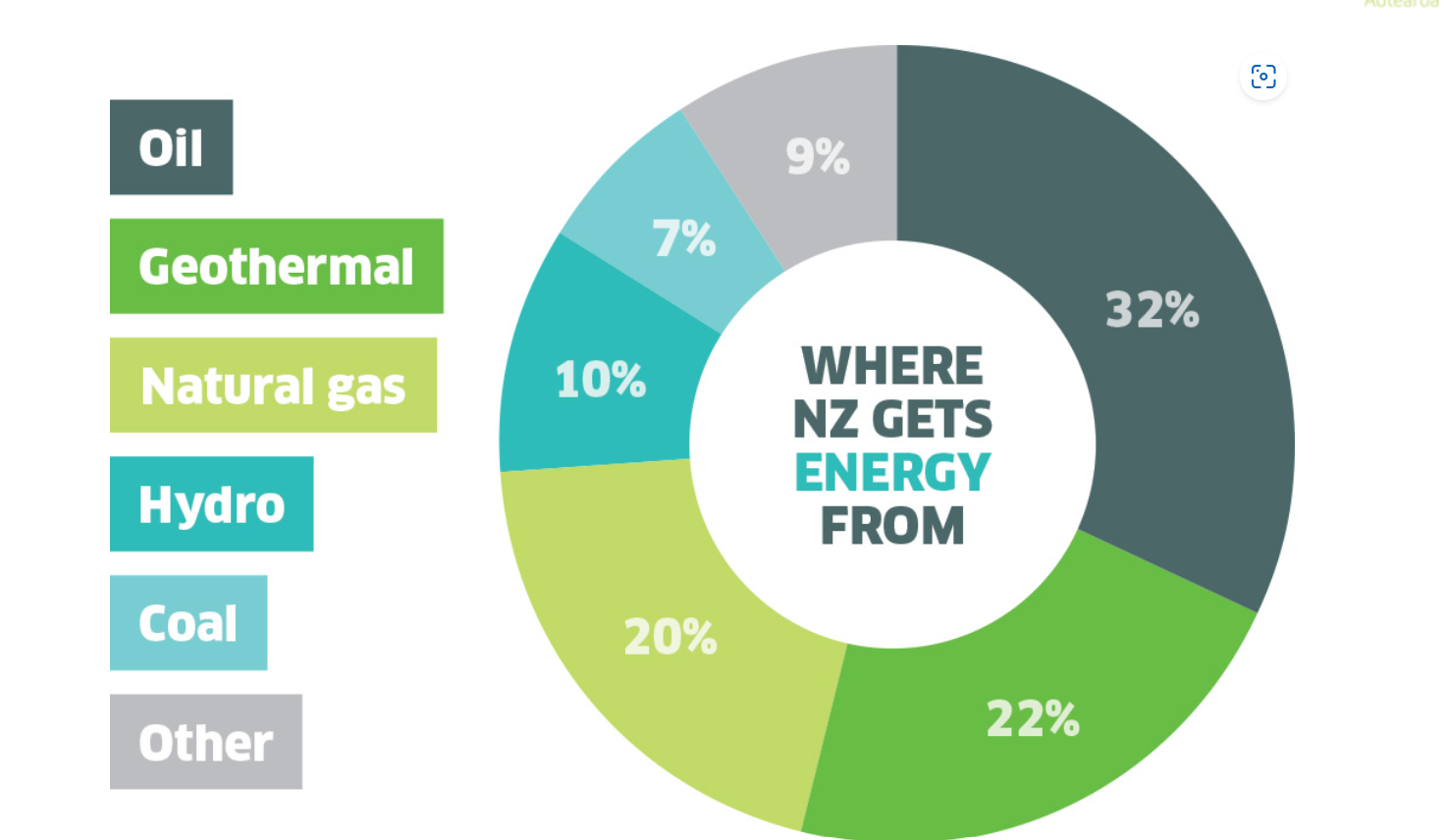
Fig 2: Energy mix of New Zealand
New Zealand has set ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, including achieving net zero emissions by 2050. New Zealand already has a low ‑ emissions electricity system, with over 80 percent of electricity coming from renewable sources in 2021. And this share could easily reach over 90 percent based on existing policies. [5]
[5] Executive summary – New Zealand 2023 – Analysis - IEA
Hydrogen has several technologically and financially viable use cases in New Zealand that could lead to a relatively high level of hydrogen demand. Though hydrogen could have many promising uses globally, only some are likely to be viable in New Zealand [6] :
▪ Hydrogen is most competitive for heavy-duty transport and as a demand response tool (provided other markets exist for the hydrogen)
▪ Hydrogen could be economic for aviation, maritime transport, and energy export, but the technology evolution is uncertain
▪ Hydrogen could also have some intermediate uses in the short to medium-term to help partially abate emissions
The Government committed to developing a Hydrogen Roadmap as part of the Emissions Reduction Plan in 2022. The roadmap will outline the Government’s position on the future role of hydrogen in New Zealand and set out the pathway for establishing a hydrogen industry in the country that will support the transition to net zero 2050. It builds on the green paper ‘A Vision for Hydrogen’, released in 2019, and forms a pillar of the forthcoming New Zealand Energy Strategy (due by the end of 2024) alongside other projects including the Gas Transition Plan, Energy Market Measures project, Offshore Renewable Energy regulatory framework project, and the New Zealand Battery Project. [7]
The Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment is currently seeking feedback on the Interim Hydrogen Roadmap, which [8] :

New Zealand’s large share of renewable electricity is largely due to favorable geography, including being an island nation with mountains, lakes, relatively consistent wind and rainfall, plus access to geothermal resources. The percentage of New Zealand’s electricity generated from renewable energy sources varies each year depending on the amount of rainfall, and to a lesser extent, the amount of wind. [9]
New Zealand currently has the fourth-highest renewable electricity percentage in the OECD, currently at around 84 percent and growing. Furthermore, the New Zealand Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment estimates there is approximately 14,700 MW of potential additional capacity – providing ample scope for investment opportunities across the clean-energy value chain. Prices are globally competitive, supported by New Zealand's high annual average capacity factors of around 50 percent for hydro, up to 95 percent for geothermal, and 40 percent for wind (which is among the highest in the world). [10]
Hydrogen projects in New Zealand [11] : -
Marsden Point Refinery and Fortescue Future Industries research MOU | An MOU announced in 2021 to jointly study the commercial and technical feasibility of producing, storing, distributing, and exporting hydrogen products from the decommissioned refinery site. |
Ports of Auckland hydrogen project | A commitment to building a hydrogen production and refuelling facility, and investing in hydrogen fuel-cell vehicles, with a goal for the Port to be zero-emissions by 2040. Japanese firm Obayashi announced its investment in the project in August 2021. |
| Hyundai NZ NEXO demonstration project | New Zealand's first hydrogen fuel-cell SUV, the NEXO, imported in 2018. |
| TR Group demo project | 20 hydrogen-fuelled trucks scheduled to be imported in 2022 to be leased to freight companies, with co-funding from the Energy Efficiency & Conservation Authority (EECA) and COVID-19 Response and Recovery Fund
|
| Hyundai Xcient hydrogen truck pilots | Hydrogen-powered fuel cell trucks imported in 2021 |
Auckland Transport hydrogen bus
| New Zealand’s first hydrogen bus, built by Global Bus Venture in 2021 |
| Kiwi H2 diesel bus conversion | Licensed technology from the United Kingdom will be used to convert diesel buses to run on 40 per cent hydrogen. The project includes funding from the EECA Low Emission Transport Fund |
| Tuaropaki Trust and Obayashi Corporation‘s geothermal hydrogen pilot study | New Zealand’s first green hydrogen plant that uses electricity generated by the nearby geothermal power plant in Taupō. |