Paraguay's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) sits around $43 billion (nominal) in 2023, placing it among the smaller economies in the region [1] .However, considering Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), which reflects the cost of living, Paraguay's GDP jumps to $118 billion, indicating a decent standard of living for its citizens.
Paraguay's economic potential lies in:
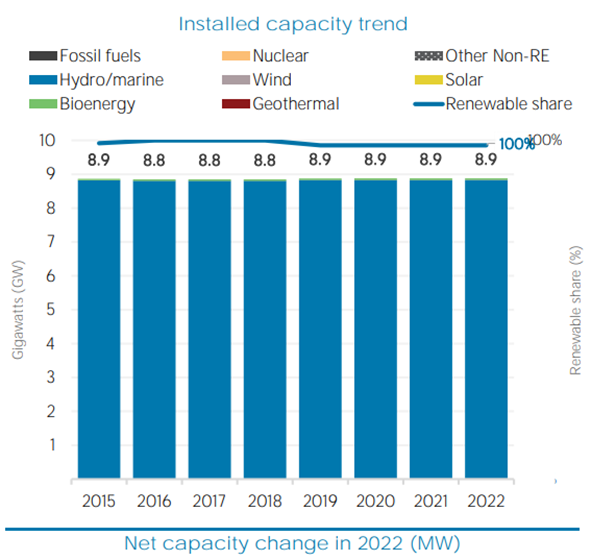
Fig 1: Installed capacity trend in Paraguay( IRENA 2022 )
Paraguay is a frontrunner in renewable energy generation, particularly hydropower. The Itaipu Dam, co-owned with Brazil, is one of the world's largest hydroelectric facilities1. Abundant water resources offer significant potential for expanding hydropower and exploring other renewables like solar and wind
Paraguay is a frontrunner in renewable energy generation, particularly hydropower. The Itaipu Dam, co-owned with Brazil, is one of the world's largest hydroelectric facilities1. Abundant water resources offer significant potential for expanding hydropower and exploring other renewables like solar and wind [2] . .A robust renewable energy sector could not only fulfil domestic needs but also solidify Paraguay's position as a clean energy exporter.
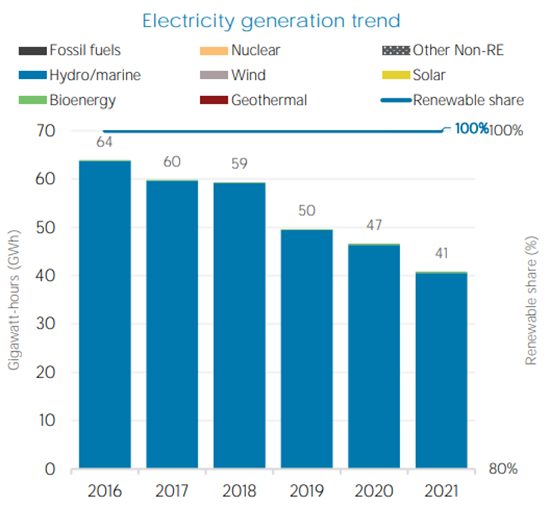
Fig 1: Electricity Generation trend in Paraguay ( IRENA 2022 )
Paraguay still grapples with challenges like poverty, inequality, and infrastructure deficiencies. Diversifying the economy beyond agriculture and attracting more foreign investment are crucial for sustained growth.
Despite these challenges, Paraguay's future looks promising. With a strong foundation in agriculture and a bright future in renewables, Paraguay can continue its path to becoming a more prosperous and sustainable nation.
Paraguay is still in the early stages of developing a hydrogen policy, with a specific focus on green hydrogen production. Paraguay does however have a strong focus on renewable energy and shows promise for developing a green hydrogen sector. Paraguay is a leader in renewable energy generation, particularly hydropower. This strong foundation provides the necessary clean electricity to produce green hydrogen through electrolysis1.
Emerging Developments: While a comprehensive green hydrogen policy isn't yet in place, there are positive indications of Paraguay's interest in this sector. In 2021, Paraguay and Germany signed a cooperation agreement to explore opportunities for green hydrogen production [1]
Overall, while there isn't a solidified green hydrogen policy yet, Paraguay's strong renewable energy sector and increasing global interest in this field make it a country to watch in terms of future green hydrogen development.
Government Initiatives:
The Vice Ministry of Mines and Energy (VMME) released a report titled "Towards the Green Hydrogen Roadmap in Paraguay" in June 2021 [2] . The report outlines ambitions for green hydrogen development by 2030, including estimated production capacity and potential uses in transportation. In addition, the Minister of Public Works expressed his interest in the transition to clean mobility. ANDE (Administración Nacional de Electricidad) will analyze the possibility of using hydrogen as a backup during peak load times. The Ministry of Industry and Commerce (MIC) will analyse the possibility of using hydrogen in industrial and productive processes, to replace the unsustainable use of Biomass.
Potential applications in the transportation sector, with studies on fuel cell electric buses are under research and development. Collaborations with international organizations like the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) are also being considered from a funding perspective.
While a comprehensive policy framework isn't established, the government's roadmap and ongoing research indicate Paraguay's commitment to exploring green hydrogen. Further development will likely require attracting investment and addressing infrastructure needs.
Hydrogen Profile [1]
In 2022, Paraguay exported $39.8k in Hydrogen, making it the 46th largest exporter of Hydrogen in the world. At the same year, Hydrogen was the 766th most exported product in Paraguay. The main destination of Hydrogen exports from Paraguay are: Bolivia ($39.8k).
The fastest growing export markets for Hydrogen of Paraguay between N/A and 2022 were Bolivia ($39.8k).
In 2022, Paraguay imported $2.02k in Hydrogen, becoming the 123rd largest importer of Hydrogen in the world. At the same year, Hydrogen was the 3643rd most imported product in Paraguay. Paraguay imports Hydrogen primarily from: Brazil ($2.02k).

Paraguay boasts significant potential in renewable energy, but its infrastructure presents both opportunities and challenges for development. Overall, Paraguay's renewable energy potential is vast, but infrastructure investments are essential to unlock its full potential. Modernizing the existing grid and expanding access will be crucial for integrating diverse renewables and ensuring a sustainable energy future.
Renewable Energy Potential
Infrastructure Challenges:
Infrastructure Opportunities:
N/A
There are several green hydrogen projects planned or announced in Paraguay, highlighting the country's growing interest in this sector. While these projects represent significant steps, it's important to note that, they are still in the planning or construction phase, and will take time to be operational. Paraguay is currently developing its national hydrogen strategy, which will provide a more comprehensive picture of future green hydrogen projects. Few prominent examples are as follows: