Spain has the 14th largest economy globally in terms of nominal GDP, with a value of USD1.44 trillion in 2023. This translates to a GDP per capita of USD30,352, ranking 41st in the world. [1] . Spain is a global leader in renewable energy use for electricity generation, aiming for full reliance on renewables by 2050.
The country is actively transitioning away from fossil fuels like coal and increasing its share of renewables in both energy supply and electricity mix. Natural gas remains the primary energy source, contributing 41.3 percent to Spain's electricity generation in 2021 [2] . Renewable energy is the second-largest source of electricity generation in Spain, accounting for 46.7 percent of the total in 2021. puts Spain as a global leader in renewable energy use. Within renewables, the breakdown is shown in the graph below:
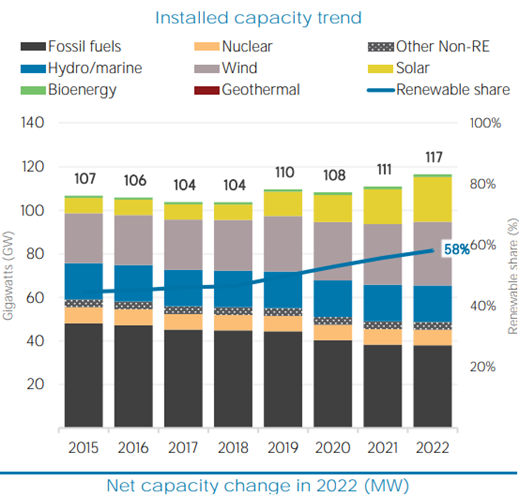
Fig 1: Installed capacity trend in Ethiopia ( IRENA 2022 )
Spain has opted to decarbonise the energy system by relying on renewable hydrogen in sectors such as industry and heavy transport, which are sectors that are difficult to electrify. Hydrogen holds potential as it be used to store energy from renewable sources to help secure supply. [3]
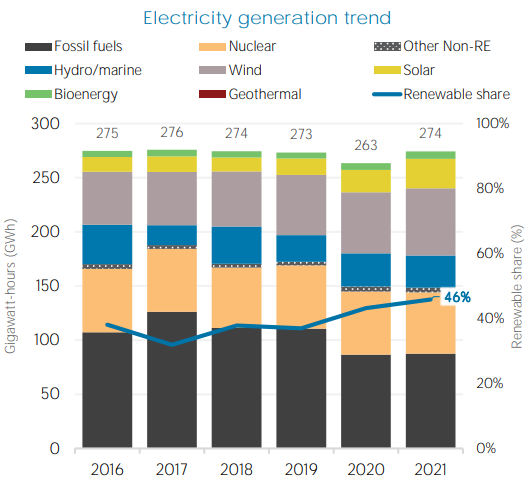
Fig 2: Electricity Generation trend in Ethiopia ( IRENA 2022 )
[3] Spain – a benchmark of renewable energies
In 2021, Spain exported USD102M in Hydrogen , making it the 22nd largest exporter of Hydrogen in the world. The main destination of Hydrogen exports from Spain are: United Kingdom (USD33M), Portugal (USD20.1M), Korea (USD9.91M), Germany (USD6.99M),and Italy (USD6.96M). The fastest growing export markets for Hydrogen of Spain between 2020 and 2021 were South Korea (USD9.8M), United Kingdom (USD9.25M), and Italy (USD5.98M). [4]
In 2021, Spain imported USD92.6M in Hydrogen, becoming the 26th largest importer of Hydrogen in the world. Spain imports Hydrogen primarily from: Netherlands (USD20.1M), China (USD16.3M), Portugal (USD14.7M), Algeria (USD12.1M), and France (USD10.5M). The fastest growing import markets in Hydrogen for Spain between 2020 and 2021 were China (USD10.6M), Netherlands (USD8.6M), and Algeria (USD4.24M).
Overall, Spain is well-positioned to become a leader in the green hydrogen sector, with growing domestic demand, significant production potential, and export opportunities. The supportive policy framework further facilitates the development and adoption of this clean energy source.
The government offers various financial incentives to attract investment and support green hydrogen projects, such as reduced corporation tax and R&D deductions, along with grants, subsidies, and feed-in tariffs. Spain actively fosters innovation and research, with Public-private partnerships and research collaborations. Fundings are allocated for research projects focusing on innovation and cost reduction in green hydrogen production, storage, and utilization.
The Spanish government is actively promoting green hydrogen development through various policy measures and has laid down the National Hydrogen Roadmap [5] , which is commitment to renewable hydrogen" (October 2020) outlines the government's strategy and sets ambitious targets:
Existing legal frameworks form a foundation for green hydrogen5:
Spain is at the forefront of developing a clear and supportive regulatory framework for green hydrogen adoption. While a comprehensive European framework is still under development, Spain has established a framework that enables:
Production:
Transportation and Distribution:

Spain's existing infrastructure and abundant renewable energy resources create a strong foundation for its clean energy transition. Addressing the challenges through targeted investments and collaborative efforts will be crucial to unlock this potential and solidify Spain's position as a leader in the renewable energy sector.
Spain has emerged as a European leader in the transition towards a renewable energy-based economy. Here are key developments highlighting this trend:
Electricity Grid [7] :
Natural Gas Grid [8] :
Ports [9] :
Investments: Investments are being made in port infrastructure to support the hydrogen economy, including bunkering facilities for hydrogen-fueled vessels.
Abundant Sunlight [10] :
Several large-scale green hydrogen projects are in various stages of development, demonstrating investor confidence and potential future growth: