Hydrogen is currently used in oil refineries to perform several crucial functions related to the refining of crude oil and conversion of the extracted crude oil into useful fuels like gasoline, diesel, kerosene and others. A series of complex chemical processes are carried out to perform specific set of activities to achieve the end-goal. Some of those oil refining processes which use hydrogen are as follows:
As per IEA’s Global Hydrogen Review, 2024, the demand of hydrogen from oil refining operations stood at 43 MMT in 2023, out of an overall demand of 97 MMT [1] . Almost the entirety of this hydrogen is sourced from fossil fuels. On-site hydrogen production accounted for 80% of the total production, while merchant procurement of hydrogen contributed to the remaining demand.
The demand is projected to reduce to 35 MMT in 2030 owing to slowdown in demand for oil, considering IEA’s net zero scenario.
Hydrogen is produced almost wholly from fossil fuels, for use in oil refining processes. Figure 1 shows some of the methods of producing hydrogen in oil refining, all of which involve the use of fossil fuels like natural gas, naphtha etc.
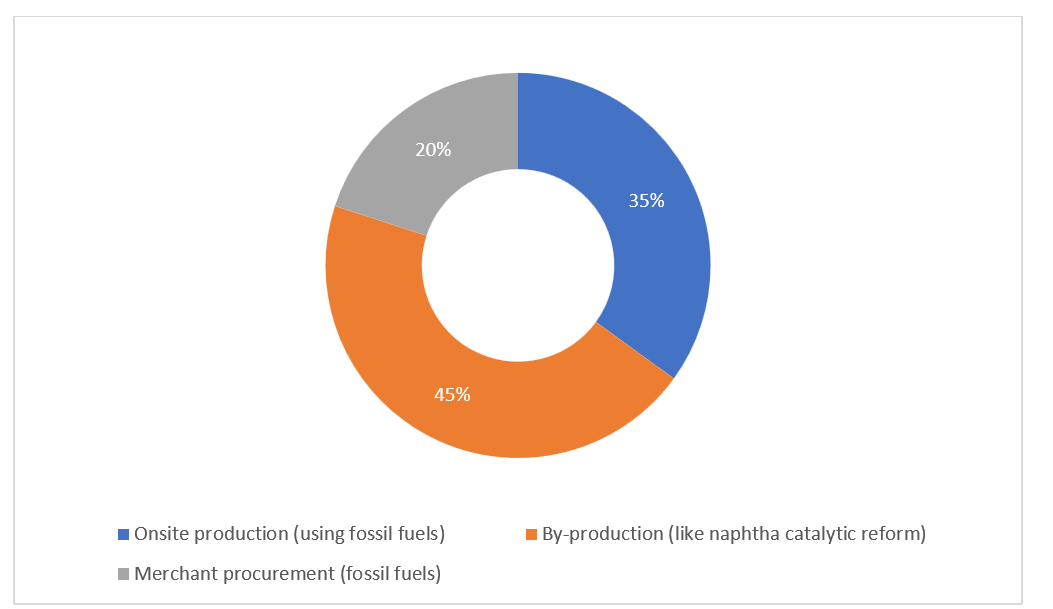
Figure 1 : Hydrogen supply sources for oil refining, 2023